331
Views & Citations10
Likes & Shares
Keywords: Foreign trade, Fiscal policy, Export, Import
The research questions are:
Does fiscal policy have an impact on foreign trade and on exports and imports?
Do the countries of the region have trade exchanges with each other?
For the finalization of this paper, the submitted material has the following support: a) Local and foreign literature, as well as reports and publications from the Ministry of Finance and the Kosovo Agency of Statistics, related to fiscal policy and foreign trade in the Republic of Kosovo. b) The local statistical source was used, the method of analysis and synthesis, tabular and graphic separately, comparative method, etc.
Theoretical Background
Kosovo’s budget process involves a large number of institutions at the central level (including Ministries and semi-autonomous public bodies) and at the local level (including municipalities and other local organizations), and remains under close observation and involvement from international organizations (including the EU, IMF, World Bank and several bilateral partners-USAID, GIZ, Denmark, Sweden). Public expenditure management is regulated by the Law on Public Financial Management and Accountability no. 03/L-048 Article 5, which is generally consistent with contemporary PMF (Public Financial Management) laws in other countries. The Ministry of Finance (MF, formerly the Ministry of Finance and Economy- MEF), is responsible for preparing the national budget, based on input received from budget organizations, including line ministries and municipalities, and related organizations (Gjokaj, Halimi, & Leeds, 2017; Agricultural Finance in Kosovo, 2017). Kosovo with an open economy in international trade is dominated by import and low level of export, resulting in this way with high commercial deficit. Aside from other macro-economic indicators also the international exchange formulates the level of the economic development of respective country expressed through the structure and value of imported and exported goods.
International trade greatly enhances living standards for all parties involved because (William, Baumol & Alan, 2010).
Every country lacks some vital resources that it can get only by trading with others.
Each country’s climate, labor force, and other endowments make it a relatively efficient Producer of some goods and a relatively inefficient producer of others.
Specialization permits larger outputs via the advantages of large-scale production.
The impact of fiscal policy on foreign trade
In international trade exchange a crucial role plays taxation. Therefore, the taxation is considered one of the instruments of the fiscal policy of great importance which affects the process of international exchange. The influence of the taxation in international exchange depends from the status and objective national economy. Indirect taxes shall mean taxes which have effect in the price of goods and services and in this way, they also have effect in international exchange of goods and services through export and import. In this course the taxation has an impact in export and import of the national economy. Taxation impacts in export and import of goods and services stimulating or de -stimulating them through the measures of taxation policy. Taxation calculated in the price of the goods and services impacts in their increase or decrease in the market. Taxation stimulates export through low taxation rates or realizing the exporters from taxation. By application of such measures of taxation policy the national export shall be stimulated. Application of measures of taxation policy as are low tax rate or clearing from taxes stimulates the national production, with a view to cut down prices of the goods and services and such prices be more competitive in the international markets. The taxation has its effect in import of the goods and services having effect as well holding up or delaying the import of goods and services. The government to protect national producers or a certain branch of the economy from the competition undertakes strict measures of fiscal policy respectively increases customs taxes, VAT rate in imports with a view to increase the prices of imported products and services protecting in this way national producers. Kosovo applies a favorable fiscal policy in the context of trade policy. Kosovo is applying a very competitive tax rate comparing to countries in the region. Besides this the taxation system is favorable for export activities. In other words, through fiscal policy it is attempted to stimulate national production and exports. While for the imports are applicable VAT, Customs tariffs and excise, excluding some of the categories of the goods which are free from the fiscal policy with the view to stimulate national production.
Characteristics of International trade Kosovo’s trade partners
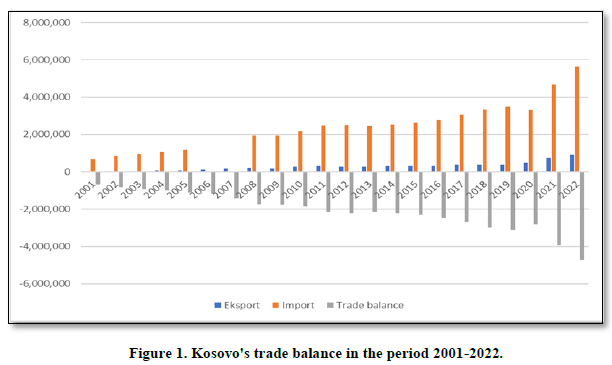
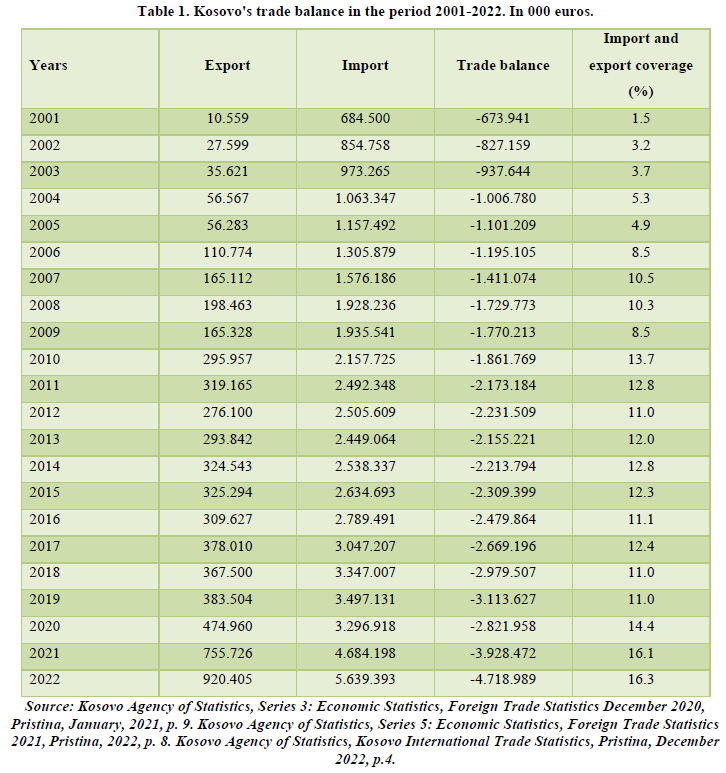
The Kosovo’s economy has had a relatively low development since 1999. Even that, during this period have been undertaken important macroeconomic steps for regeneration of Kosovo’s economy, still there are many challenges. One of the indicators is a high negative and constant commercial balance since 1999. Since the post conflict period the low level of economic development of Kosovo that in economic relations to dominate the import of goods and services which evidently is higher than export and impacts in a high deficit of payment balance. Kosovo in a post conflict period has commercial relations with different countries in a region and worldwide. Regarding to the commercial relations with other countries, Kosovo since the post conflict period is very devoted for trade liberalization. However, economical exchange with other countries for Kosovo’s economy since the post conflict period is reflected as unhandy. This is for the fact that the low level of Kosovo’s economic development is reflected that in economic relations dominate import of goods and services which evidently is higher than export and, in this way, impacts in a higher deficit of commercial balance. This can be concluded through the reflection of international exchange of Kosovo with other countries as it is shown in the Table 1 below. The table below represents Kosovo’s economic relations with other countries in a period of time from: 2001-2022.
Looking at foreign trade, the performance of exports and imports show that Kosovo has a low level of economic development. Imports make up the bulk of Kosovo's trade exchange. Foreign trade in Kosovo since the post-war period has had increasing trends in exports and imports. Despite the increase in exports, the low export base has a relatively low impact on reducing Kosovo's trade deficit (Figure 1).
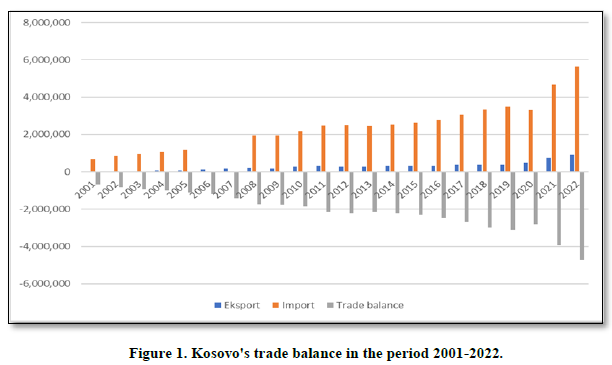
From the table and graph, there is a trend over the years in the expansion of trade activity, but despite the increase in exports, the significant increase in the dominance of imports continues. The export performance from the period 2001-2022, increased from 10.5 million euros as it was in 2001, to 920.4 million euros in 2022, while the import from the period 2001-2022, increased from 684.5 million euros as it was in 2001, in 5.6 billion euros in 2022. The performance of exports and imports in post-war Kosovo is an indicator that reflects the level of development in the country, and the dominance of imports over exports results in a high trade deficit. The trade deficit in 2001 was -673.9 million euros, reaching -24.7 billion euros in 2022. Total exports in 2021 were 755.7 million euros, while imports 4.6 billion euros. The year 2021 turned out to be with a degree of coverage of imports with exports of 16.1 percentage points, while in 2022, exports were 920.4 million euros, imports 5.6 billion euros. The year 2022 turned out to have a degree of coverage of imports with exports of 16.3 percentage points. Such a relationship between imports and exports leads us to the conclusion that, in Kosovo, most of the material goods to meet the needs of the population, are imported from abroad from which we can draw two findings
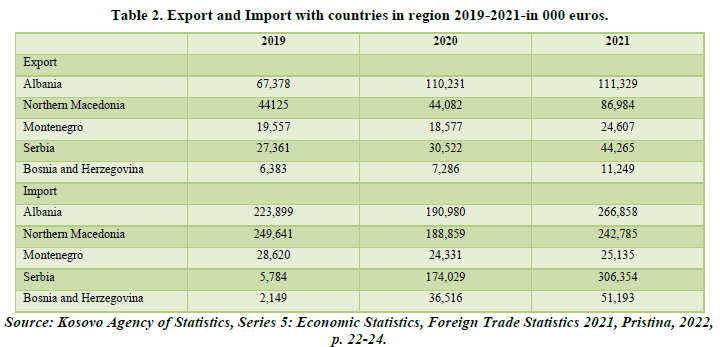
First, we are dealing with low level of economic development and second, through imports, development policy makers have wanted to more easily fill Kosovo's budget coffers (Table 2).
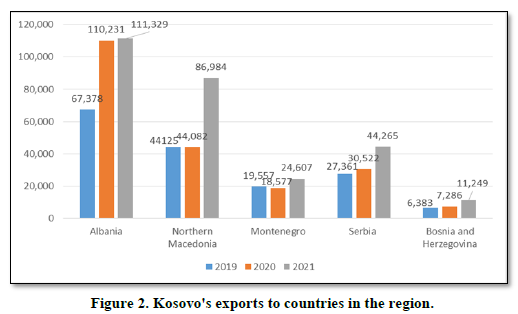
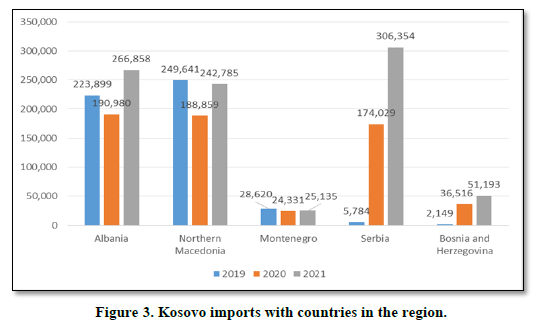
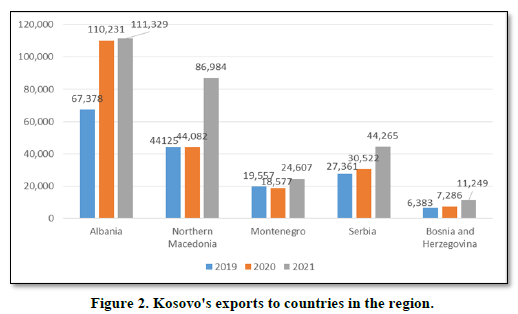
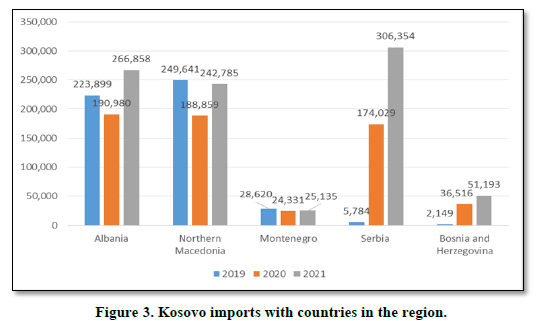
The Figures 2 & 3 shows the performance of Kosovo's exports and imports with the countries of the region in the period 2019-2021. Kosovo in terms of countries in the region mainly exports more to Albania in the amount of 111.3 million euros in 2021 and Northern Macedonia in the amount of 86.9 million euros in 2021. While in terms of imports mainly imports more from Serbia in value of 306.3 million euros in 2021 and from Albania in the amount of 266.8 million euros.
CONCLUSION
Kosovo in the period after the conflict started to build an open market economy. Kosovo is devoted to liberalize the trade where the participation in regional mechanisms and worldwide shall facilitate trade was one of the main objectives of policies of the Kosovo’s Institutions. In Kosovo’s commercial exchange it is evident the negative commercial balance where the import is dominating comparing to export. Even that during this period have been taken important macro-economic steps for renewal of Kosovo’s economy, still there are many challenges. There are many reasons for such poor performance in the export sector in Kosovo, therefore one of the factors which should be specified and which has had impact in develop0ment of enterprises and in particular export sector are: Kosovo after the conflict has inherited companies and industries almost in total collapse as a result of abductions and destructions, delays in the process of privatization, unsatisfactory level direct foreign investments as a very important factor in many countries in transition for renewal of economy and in particular export sector. Then informal economy, non-systematic supply with energy and limited road infrastructure remains main factors having impact in economic development of the country. Disproportions in international trade generate macro-economic disproportions with long -term implications in a sustainability and economic growth of Kosovo. Herewith the reduction of these disproportions should be a long-term priority. Economic policies and in particular fiscal policies must be in focus to exceed this situation and growth production and also to growth of competition capabilities and promotion of export through better and more favorable actions in the future. Therefore, reform of fiscal policy should be oriented in stimulation of national production. In this way by encouraging of national production can be founded conditions to decrease the level of the dependence from the foreign market, a wide assortment of products be offered in the international market as the result of this there will an improved commercial balance. 165 term priority. Economic policies and in particular fiscal policies must be in focus to exceed this situation and growth production and also to growth of competition capabilities and promotion of export through better and more favorable actions in the future. Therefore, reform of fiscal policy should be oriented in stimulation of national production. In this way by encouraging of national production can be founded conditions to decrease the level of the dependence from the foreign market, a wide assortment of products be offered in the international market as the result of this there will an improved commercial balance.
William Baumol, J., & Alan Blinder, S. (2010). Economics- Principles & Policy.
Skender, B. (1994). International Economic Relations, Pristina.
Gjokaj, E., Halimi, K., & Leeds, S. (2017). Agricultural Finance in Kosovo.
Ministry of Trade and Industry (2009). Kosovos Trade Policy Pristina.
Kosovo Agency of Statistics (2022) Kosovo International Trade Statistics Pristina.
Kosovo Agency of Statistics (2021). Series 3 Economic Statistics Foreign Trade Statistics Pristina.
Kosovo Agency of Statistics (2022). Series 5 Economic Statistics, Foreign Trade Statistics Pristina. Available online
at: https://ask.rks-gov.net/media/7266/international-trade-statistics-december-2022.pdf
Kosovo commercial policy (2009). Ministry of Trade and Industry Pristina.
Komoni Sabahudin (2008). Public Finances Pristina.
Kosovos Tax Legislation, (2015). ATK Pristina.